Intersection observer and infinite scroll in a visual way
Infinite scroll in a visual way
Most implementations of infinite scroll involve listening to the scroll event. But that triggers too many times, and you also need to make some calculations to check if the user is at the bottom of the page.
const onWindowScroll = () => {
console.log('scroll');
const reachedBottom = isAtTheBottom();
if (reachedBottom) getMoreItems();
};const onWindowScroll = () => {
console.log('scroll');
const reachedBottom = isAtTheBottom();
if (reachedBottom) getMoreItems();
};You could use the throttle or debounce to optimize it, but it's still not ideal.
A better solution is to put an element at the bottom of the page and use the IntersectionObserver to be notified when the element enters the view.
If that short version was enough for you, just leave a like and have a great day! Heck, you could even drop a tweet, if you want me to have a great day.
If you stick around, I'll show you an infinite scroll implementation using scroll events, then we'll optimize its performance with throttling and debouncing, and in the end, I will show you how to make it even better using the IntersectionObserver.
This is the implementation using scroll events, here's how it works:
We have a getItems(amount, pointer) function that returns a promise of an array of items to show. We can specify the number of items we want to get, and we can also give it a pointer, which is just a number indicating the last item we got.
export const getItems = async (
amount: number,
pointer: number = 0
): Promise<{ items: Array<Item>; pointer: number; hasMore: boolean }> => {
// Wait a second to simulate delay
await new Promise((res) => setTimeout(res, 1000));
// Get items
const itemIndexes =
const items = Array.from({ length: amount })
.map((_, i) => i + pointer)
.map((index) => ITEMS[index] ?? null)
.filter((v) => v !== null);
const lastPointer = items.length + pointer;
const hasMore = lastPointer < ITEMS.length - 1;
return { items, pointer: lastPointer, hasMore };
};export const getItems = async (
amount: number,
pointer: number = 0
): Promise<{ items: Array<Item>; pointer: number; hasMore: boolean }> => {
// Wait a second to simulate delay
await new Promise((res) => setTimeout(res, 1000));
// Get items
const itemIndexes =
const items = Array.from({ length: amount })
.map((_, i) => i + pointer)
.map((index) => ITEMS[index] ?? null)
.filter((v) => v !== null);
const lastPointer = items.length + pointer;
const hasMore = lastPointer < ITEMS.length - 1;
return { items, pointer: lastPointer, hasMore };
};When we receive the items, we create a card for each and request more items when the user scrolls to the bottom of the cards list.
To see if the user is at the bottom, we listen to scroll events in the document, and then we run a function called isAtTheBottom() which returns true if the user is at the bottom.
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
const reachedBottom = isAtTheBottom();
if (reachedBottom) {
// Get the items
const items = getItems(...);
// Render a card for each item
renderCards(items);
}
})window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
const reachedBottom = isAtTheBottom();
if (reachedBottom) {
// Get the items
const items = getItems(...);
// Render a card for each item
renderCards(items);
}
})isAtTheBottom() is the only relevant function so far, the rest of the implementation is just styling, rendering the cards, and a loading spinner. But if you're curious, I'll leave a link for the repository in the references.
export const isAtTheBottom = (margin = 0): boolean => {
const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight;
const pageHeight = window.document.body.scrollHeight;
const pageScrollY = window.scrollY;
const pixelsToReachBottom = pageHeight - (pageScrollY + viewportHeight);
return pixelsToReachBottom - margin <= 0;
};export const isAtTheBottom = (margin = 0): boolean => {
const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight;
const pageHeight = window.document.body.scrollHeight;
const pageScrollY = window.scrollY;
const pixelsToReachBottom = pageHeight - (pageScrollY + viewportHeight);
return pixelsToReachBottom - margin <= 0;
};
As I've said in the beginning, scroll events trigger too much. And we call isAtTheBottom() every time a scroll event triggers.
Here, I'll scroll to the bottom of the page and log every time a scroll event triggers. Look how many they are. { amount } events just now.
I already gave you a spoiler, you know we're going to ditch the scroll events. But before doing that, I'll show two optimizations we could make to drastically improve the performance while still listening to scroll events.
The first one is throttling.
Define a duration, say 100 milliseconds for example.
Throttling the scroll events by 100 milliseconds means letting a scroll event pass, then ignoring all other scroll events for the next 100 milliseconds.
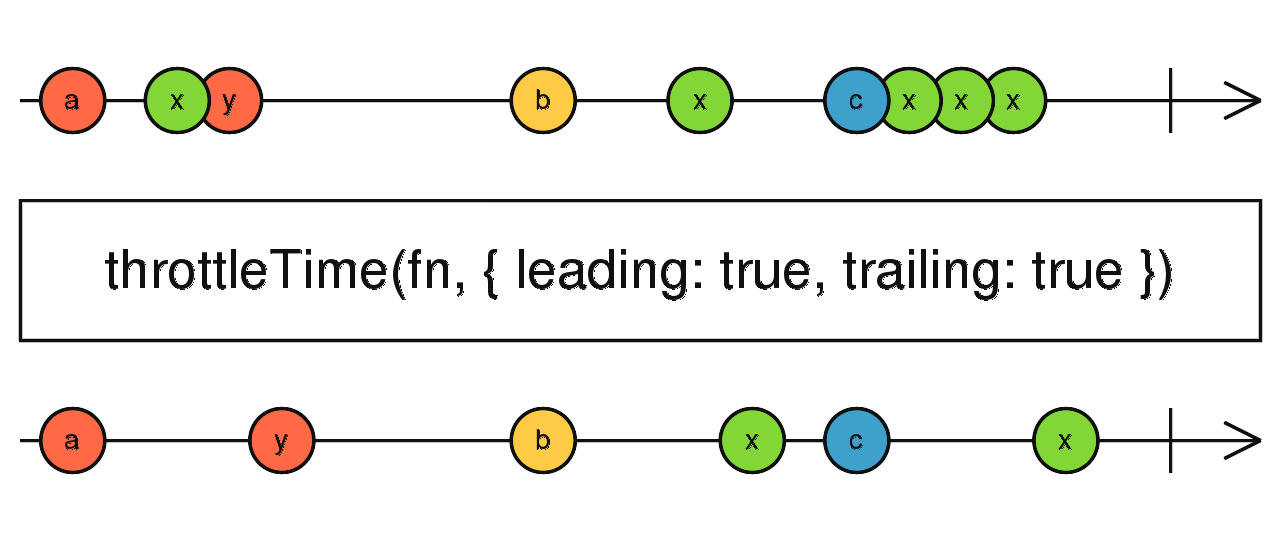
To use throttling we can create a higher-order function.
To summarize, in case you don't know what that is, a higher-order function is a function that receives a function and returns another function. It can be hard to understand at first, I'm writing a book about functional programming and this is one of the topics I'll be covering in the book. Quick plug, you can
// Example of a higher order function
export const logDuration =
(fn) =>
(...args) => {
console.log('start', Date.now());
fn(...args);
console.log('end', Date.now());
};// Example of a higher order function
export const logDuration =
(fn) =>
(...args) => {
console.log('start', Date.now());
fn(...args);
console.log('end', Date.now());
};Anyway, back to throttling.
A simple implementation of throttling in javascript could be the following:
const throttle = <F extends (...args: Array<any>) => void>(
fn: F,
duration: number
): ((...args: Parameters<F>) => void) => {
let waiting = false; // Initially, we're not waiting
return function (...args: Parameters<F>): void {
// We return a throttled function
if (waiting === false) {
// If we're not waiting
fn.apply(this, args); // Execute users function
waiting = true; // Prevent future invocations
setTimeout(() => {
// After a period of time
waiting = false; // And allow future invocations
}, duration);
}
};
};const throttle = <F extends (...args: Array<any>) => void>(
fn: F,
duration: number
): ((...args: Parameters<F>) => void) => {
let waiting = false; // Initially, we're not waiting
return function (...args: Parameters<F>): void {
// We return a throttled function
if (waiting === false) {
// If we're not waiting
fn.apply(this, args); // Execute users function
waiting = true; // Prevent future invocations
setTimeout(() => {
// After a period of time
waiting = false; // And allow future invocations
}, duration);
}
};
};That implementation is very simplified. I do not recommend using it. Lodash has a great throttle implementation that is battle-tested and much more complete. Use Lodash.
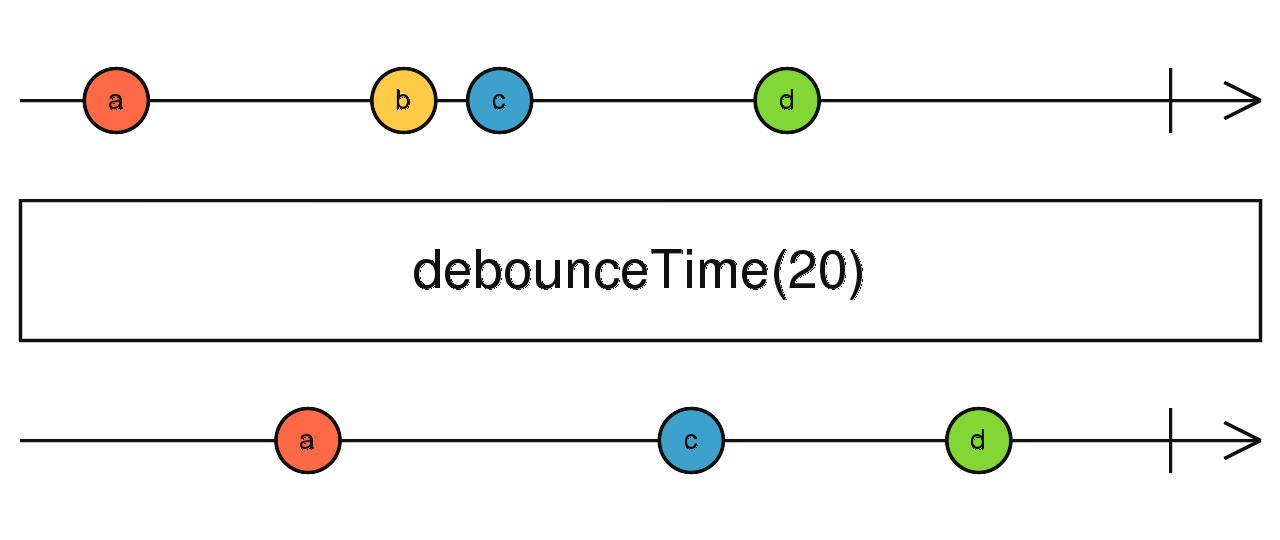
Lodash also has debounce, which is similar to throttle. They are so similar that if you enable some options in Lodash's debounce implementation, you get throttle.
Since you can use options to make them behave the same way, the differences I'm about to present are considering debounce with no options, Only it's default behavior.
Debouncing the scroll events by 100 milliseconds means only letting a scroll event pass after 100 milliseconds has passed without scroll events.
Think of them like you're swimming in a pool and every light bulb is an event. If you're throttling, you get to breathe once in a while. But if you're debouncing, you only get to breathe after a long enough space with no light bulbs.
So, which one is better? Throttling or debouncing? It depends on your use case. If you're indeed swimming, I recommend throttling.
I won't go deeper into those two techniques, but I'll leave a link in the references for David Corbacho's article on CSS Tricks where he does a great job explaining how they work and their use cases. Go, David.
So far, we've been listening to scroll events and checking if the user is at the bottom of the page.
Now, let me ask you a question: do we care about scroll events? No.
We only care about whether the user is at the bottom of the page. Scroll events are just a warning that the user has changed their position. We could ignore scroll events altogether and run our check every second, it would work just fine.
So, instead of listening to scroll events, or an interval, or whatever else. Maybe we can be more direct. What if we could listen to when the user reaches the bottom of the page? That's all we want to know, right?
And we can do that using the IntersectionObserver.
The IntersectionObserver observes intersections between elements and the viewport.
Imagine that you're on a page. The viewport is the part of the page that is currently visible. As you scroll up, the viewport goes up. As you scroll down, the viewport goes down.
Now, suppose you have an element below your viewport. As you scroll down, that element will intersect with the viewport, triggering the IntersectionObserver.
By default, the IntersectionObserver triggers as soon as even one pixel of your element is visible. You can change that behavior with the threshold option. You can tell it to trigger only when 100% of the element is visible or to trigger every 10%, or every 25%, you name it.
For our purposes, we want to know when the user reaches the bottom of the page. So we will add an element to the bottom of the page and listen to intersections on that element. As soon as 1 pixel of that element becomes visible, we request more items.
const intersectionObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {
const isIntersecting = entries[0]?.isIntersecting ?? false;
if (isIntersecting) this._getMoreItems();
});
const bottomElement = document.querySelector(...);
intersectionObserver.observe(bottomElement);const intersectionObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {
const isIntersecting = entries[0]?.isIntersecting ?? false;
if (isIntersecting) this._getMoreItems();
});
const bottomElement = document.querySelector(...);
intersectionObserver.observe(bottomElement);That's way more performant and declarative than using scroll events.
There’s another thing I like to do when I’m implementing infinite scroll. Instead of requesting more items when the user reaches the bottom, I like to request more when the user is close enough to the bottom. 100 pixels from the bottom, for example.
To do that, we can add a top margin of 100 pixels to our intersection observer using the rootMargin option.
const intersectionObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {
const isIntersecting = entries[0]?.isIntersecting ?? false;
if (isIntersecting) this._getMoreItems();
}, { rootMargin: "100px 0 0 0" });
const bottomElement = document.querySelector(...);
intersectionObserver.observe(bottomElement);const intersectionObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries) => {
const isIntersecting = entries[0]?.isIntersecting ?? false;
if (isIntersecting) this._getMoreItems();
}, { rootMargin: "100px 0 0 0" });
const bottomElement = document.querySelector(...);
intersectionObserver.observe(bottomElement);
Regarding browser support, the IntersectionObserver is available in all major browsers, and you can use a polyfill if you need to support older browsers.
There’s one more option to customize the IntersectionObserver. We don’t need to use that option for infinite scroll, but I’ll explain it to you for completeness.
Suppose you have a scrollable element, and you want to listen to intersections between that element and one of its child elements. Got it? In that case, you don't want to observe intersections between an element and the viewport, you want to observe intersections between two elements. You can do that using the root option.
const outerElement = document.querySelector(...);
const intersectionObserver =
new IntersectionObserver(callback, { root: outerElement });
const innerElement = document.querySelector(...);
intersectionObserver.observe(innerElement);const outerElement = document.querySelector(...);
const intersectionObserver =
new IntersectionObserver(callback, { root: outerElement });
const innerElement = document.querySelector(...);
intersectionObserver.observe(innerElement);One restriction here is that the root element needs to be a parent of the elements you want to observe.
If you don’t specify the root (or set it to null), it will use the viewport.
If you read our articles, you know that we use Angular a lot. To make our lives easier, we’ve created a directive to listen to intersection events.
It's available in our Angular utilities library, just import { IntersectionObserverModule } from '@lucaspaganini/angular-utils' and use the (lpIntersection)=“onIntersection($event)” directive in your templates. You can also pass intersection options with the [lpIntersectionOptions]=“options” parameter.
import { IntersectionObserverModule } from '@lucaspaganini/angular-utils'
@NgModule({
...
imports: [ ..., IntersectionObserverModule, ... ],
...
})import { IntersectionObserverModule } from '@lucaspaganini/angular-utils'
@NgModule({
...
imports: [ ..., IntersectionObserverModule, ... ],
...
})<div
(lpIntersection)="onIntersection($event)"
[lpIntersectionOptions]="options"></div><div
(lpIntersection)="onIntersection($event)"
[lpIntersectionOptions]="options"></div>
I’ll leave a link for the repository in the references.
As I was writing this article, I started to wonder if there’s a way to implement infinite scroll without adding an element to the end of the list. If you have a solution for that or anything else to contribute, please, send a tweet.
You can also hire us. We're not an agency, we're a team, and I'm personally responsible for every project. We have a limited amount of clients because I'm human, and I need to sleep. But right now, we're available, so go to lucaspaganini.com and tell me, how can we help you?
Have a great day and I'll see you soon